The tax could be a source of revenue for a government of a rustic, through which it endeavours to produce better infrastructure, the standard of living and security for its inhabitants.
However, these taxes can sometimes be available in the way of personal development of people or an organization and further push these individuals and huge business houses to contemplate the way to avoid the identical by using loopholes within the laws and guidelines that govern the taxes.

Indian government has always been proactive in closing and fixing loopholes within the tax laws and its structure through budget, amendments, guidelines and treaties with various countries. However, government during this regard is usually two steps behind the big business houses in India
According to a paper by Alex Cobham & Petr Janský, (Cobham, 2018) every year globally, around INR 50,000 crores worth of presidency revenue is lost because of tax avoidance by business sector houses. Reliance India Limited, Tata Industries, Vodafone, Google, etc. are certain potential Examples of large business houses involves in tax avoidance that function in India and who have successfully mastered the art of tax avoidance.

General Anti-Avoidance Rule (GAAR) was included in Chapter X-A of the revenue enhancement Act, 1961. GAAR was introduced in the taxation Act, by the Finance Act, of 2012, yet came into effect on the 1st day of April 2017.
The only real purpose of introducing GAAR was to curb avoidance strategies through a provision “Section 96. Impermissible avoidance arrangement”, which was embedded in the taxation Act. in keeping with the availability, arrangements or deals made so as to get a tax write-off was impermissible.

Amendment of section 6(3) of Finance Act, 2015 was drained in order to switch a replacement test of corporate residence, which only if the place of effective management (POEM) is found to be situated in India, then a far off company are a tax resident of India.
Before this amendment, for tax purposes, a corporation that wasn’t a resident of India was only considered resident, if it had been controlled and managed in India.

The Indian government 2017 took various steps to align the principles and guidelines as per the bottom erosion and profit shifting (BEPS) suggested by The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), which could curb the menace of avoidance, which has BEPS action plan 13, 1 and 5.
Tax avoidance strategies utilized by these large corporations indeed help them save billions of dollars every year, however, avoidance causes a stack of losses to the govt. and creates an unfair market, as someone working for a salary or a little business, has little knowledge or intellect for building up strategies so as to avoid taxes and find yourself paying taxes fully.
Whereas, business sector houses still lower their burden on tax through avoidance. it’s difficult to prove that these corporate giants did actually evade tax as they somehow hump in within the four law walls.
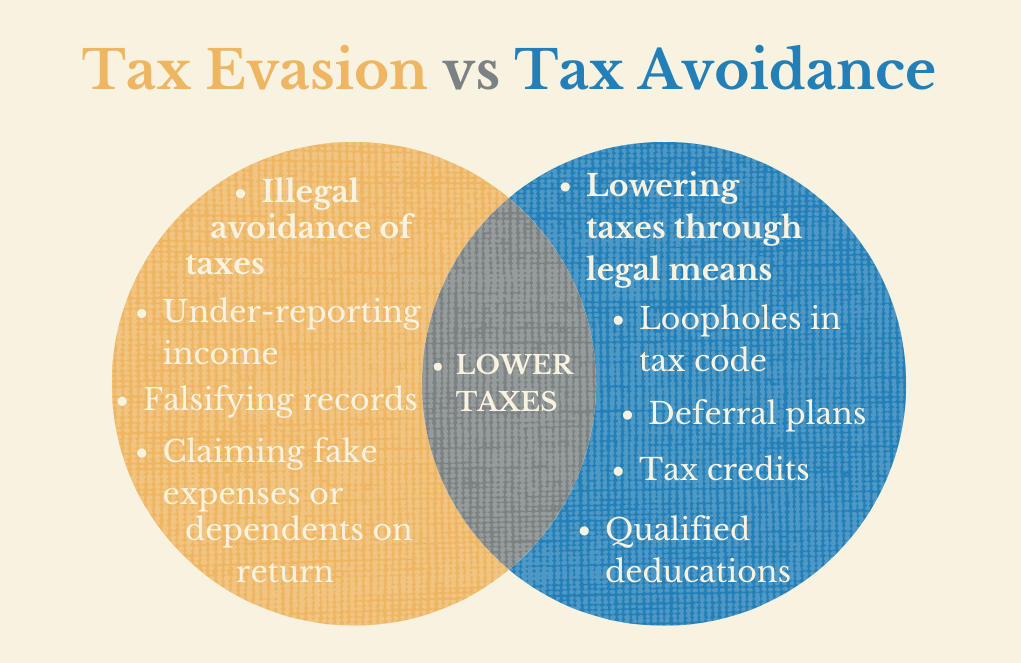
In reality, the business model of those business houses is literally supported by how effectively they will avoid tax and make huge profits for their investors.
The concept behind avoidance still remains that, other than the transaction/deal, the corporate must make a decent amount of profit and not lose a huge percentage of the profit in taxes.
In this regard, many countries have lowered tax rates to cater to the wants of those companies who reciprocally help these countries develop. Therefore this particular nexus gives effective assistance in avoiding billions worth of Rupees in taxes, thereby making minimization or avoidance advantageous to business sector houses.

