The ministry of electronics and information technology (MeitY) has unveiled the National Strategy for Additive Manufacturing Policy. The coverage goals are to grow India’s proportion in international additive production to 5% within the subsequent 3 years and upload USD 1 billion to the gross home product.

Further, its goals are to broaden 50 India precise technology for material, gadgets and software programs, one hundred new startups for additive production, 500 new merchandise and teach a minimum of 1 lakh new professional people.
The policy postulates the tenets of ‘Make in India’ and ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan’ that endorse self-reliance via the technological transformation of the manufacturing paradigm.
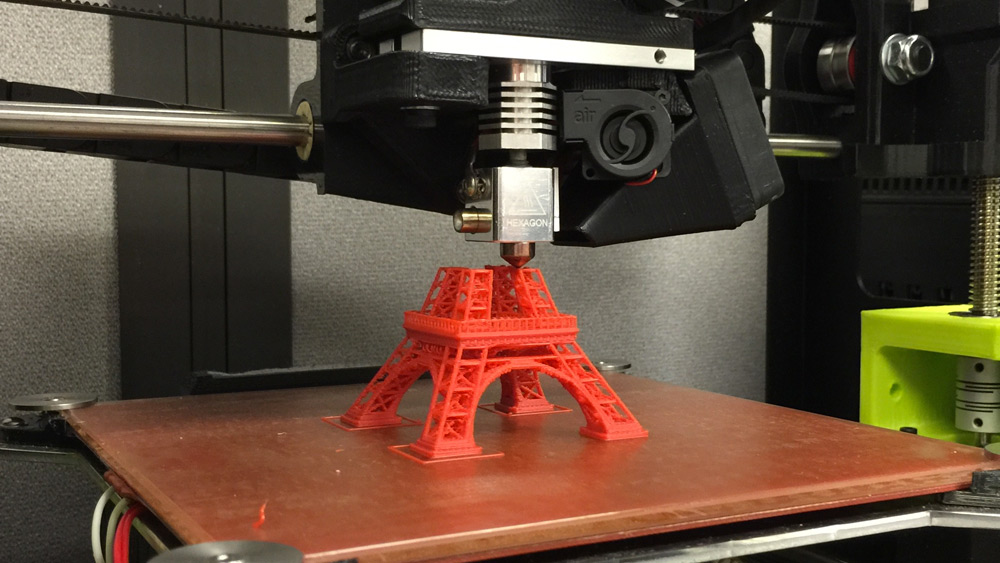
3-D printing is likewise called additive production which makes use of substances including plastics and metals to transform merchandise envisaged on the computer-aided layout into actual 3-dimensional items.
3-d printing is the other subtractive production that’s reducing out/hollowing out a bit of metallic or plastic with, for instance, a milling gadget.
Additive Manufacturing is the subsequent technology of virtual production that permits the intersection of computing electronics, imaging and the rising regions of Artificial Intelligence, sample reputation and could create highbrow assets and export opportunities.
Additive Manufacturing (AM) has a monstrous ability to revolutionize India’s production and business manufacturing panorama via virtual processes, communication, imaging, structure and engineering. The subsequent wave of startups will emerge in this area. Usage: 3-d printing historically has been used for prototyping. 3-d printing has a number of scopes for making synthetic limbs, stents, dental crowns, elements of vehicles and customer goods, amongst others.

Eliminating Large Capital Investments: Machines are cheaper, inventories may be small and area necessities aren’t big. Thus, jump-beginning production does now no longer face the large hurdle of big capital requirements and the conventional small and medium establishments can without problems be tailored and retooled toward excessive generation production.
Since 3-D printing is a total area of interest and a new domain, there aren’t any international qualifications and certification norms.

Another project is to persuade the enterprise and ministries to push for the adoption of their respective sectors as any new generation, which isn’t always understood without problems, faces a hard time.
Risk of Job Losses: In the preliminary conferences on the subject, there has been a number of resistance on whether or not this generation could consume into the roles of highly-professional people withinside the clinical gadget or aerospace generation sectors.
High Costing: Although real printing is cheap, elements to construct a 3-d printer are very highly priced because the gadget and production fees are very excessive. In addition, there’s a subject approximately assurance hence, aid agencies are hesitant to place 3-d-revealed elements into their machines if they may be now no longer included for harm in case the elements fail.

Sector Specific Challenges: Globally or even in India, the most important customer of 3-d printing is the automobile enterprise and proper now it’s miles going via a number of adjustments just like the creation of BS-VI and electric-powered vehicles. New automobile layout improvement has slowed and so has the call for 3-D printing.

